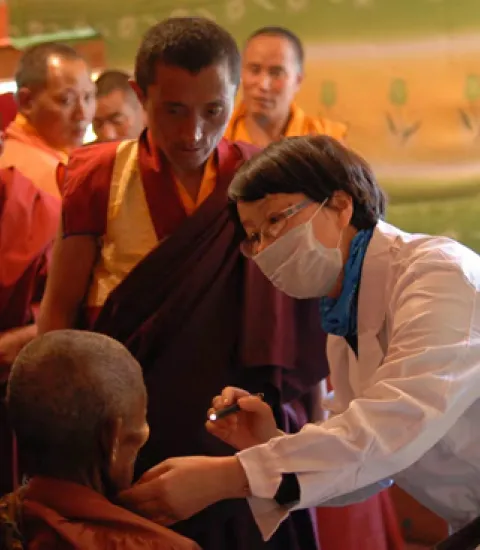
Eye Health Volunteer Service Project for people in Sichuan, Tibet and Qinghai province
The medical assistance includes general health examinations, ophthalmopathy screenings, medical diagnosis and treatments, and ophthalmic surgeries for patients with cataract or pterygium blindness/visual impairment, by establishing medical treatment stations, temporary medical clinics, and implementing mobile operating vehicles. To help establish a sustainable eye health service system in Sichuan-Tibet plateau, an “Ophthalmology Medical Service Capability Enhancement Plan" was initiated and implemented, volunteers co-established medical center, developed online platform and provided short-term trainings to local residents, doctors and nurses to enhance their knowledge about eye protection.
In addition, since 2018, this project deployed volunteers to Africa and provided ophthalmology medical services aid in Burkina Faso, Bangui in Central Africa. The project has been highly appraised by the Chinese Embassy in Burkina Faso and the Minister of Health of Burkina Faso.
Relying on the professional advantages of the Eye Optometry Hospital affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, the project aims to improve the plateau medical service capabilities, with the prevention and treatment of blindness as the main approach, to establish a comprehensive, high-performance, and sustainable eye health service in plateau Tibetan areas.
Throughout eight years of implementation since 2012, the project benefited 16 impoverished counties and cities, provided physical and eye examinations for 30,039 local people, performed 3,311eye surgeries and trained 16 Tibetan ophthalmologists, established 11 joint ophthalmology centers, eight online remote platforms, three ophthalmic operating rooms, and set one classroom for low vision people. In 2019, their Africa Aid project implemented ophthalmopathy screenings for 590 people in 17 days, medical volunteers diagnosed 232 cataract patients, and performed 221 cataract surgeries. The average age of the beneficiaries was 64 years old, the youngest was seven years old and the oldest was 89. The volunteer group has significantly improved the eye health of local people.
The eye optics centers of Tibetan hospitals supported by the project are all operating well. As of the end of 2019, the Eye Optometry Center assisted by the project has carried out a total of 66,500 eye examinations, 51,300 outpatient visits, Optometry for 1,233 people, and performed more than 2,450 cataract surgeries.
Besides, the project integrated with the college students' innovation and entrepreneurship. According to the local context, the volunteer group developed a plateau-specific ophthalmology examination toolkit, eye health examination system and eye surgery teaching aids tools. The project obtained 10 national patents. It is the only team that won the first prize in the China Division of the GSVC Global Social Enterprise Competition and the first prize in the "Internet +" National Innovation and Entrepreneurship Competition.
1. Innovative financial aid methods. Since the implementation of this project, more than 3000 case of blindness-prevention cataract surgery have been carried out. According to different income condition of the patients, the cost of the surgery could be waived. For poor and specific populations with precision poverty certificates issued by the government, all expense can be waived. For normal patients, a tripartite funding method of medical insurance, public welfare and reduced own expenses is adopted.
2. Innovative implementation methods. Instead of merely providing services, the project aims at training local medical professionals and medical care staff to strengthen the local medical capabilities and achieve the SDGs.
3. New models of partnership. During the implementation period, the project developed a new pathway of "cooperating with government, supporting the construction of the medical centers, and training talents".
Contact:
Sheng YE
Deputy secretary of Communist Youth League
Wenzhou Medical University
+86 13806688665
Links:
Wenzhou Medical University provides assistance to communities in mountainous areas of China
Illuminate the Ubangi River- Record of China’s “Bright Journey” Aid central Africa project in 2019
Video- Eye Health Volunteer Service Project for people in Sichuan, Tibet and Qinghai province