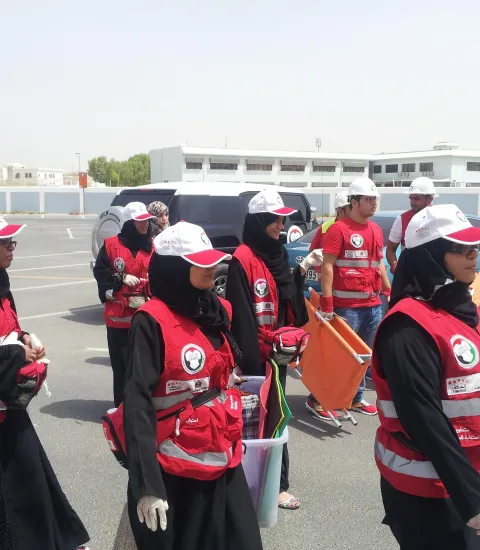
Embedding volunteers into national disaster risk reduction planning
The 2015 -2030 Sendai Framework for Disaster Risk Reduction recognizes and reaffirms the urgent need to reduce disaster risks to achieve the SDGs. The UAE is rapidly urbanizing in areas prone to floods and earthquakes. The SANID programme represents a joint private and public sector national effort to harness the skills, local knowledge, and networks of citizens to strengthen community disaster preparedness, one of the four priority areas of the Sendai Framework. While SANID expert volunteers support official rescue organizations, private sector employees and over 19,000 community members have been given basic training in safety and emergency preparedness to ensure that responses are multi-layered and cross-sectoral (SDG 11.b). These efforts, along with the development of a new national disaster risk reduction strategy and early warning systems, has helped the UAE receive praise from the United Nations Office for Disaster Risk Reduction for being a ‘leading country’ in implementing the Framework.
- Volunteers almost always play an essential role in disaster responses, however their efforts can sometimes hinder official response efforts due to lack of coordination. The SANID programme works closely with NCEMA and has established dedicated focal points in official emergency response actors to improve communication and coordination during responses.